Anna Agnieszka Czerwinska
Just like energy systems evolve from vertically coordinated grids based on centralized generation into flexible, participative and distributed structures, in a similar way the learning process is becoming more and more interactive and multidisciplinary. Learning solely based on traditional methods – passive listening to the lecturer or reading a textbook – is no longer appealing to students. At the same time, progressing digitalisation offers a broad range of new possibilities, not only to make learning efficient, but also to increase the motivation and interest of students. In response to this emerging trend, active learning has a profound effect on how to teach today.
What is active learning and how it is used
Active learning has gained a lot of attention with regard to successful knowledge transfer. In this approach, the learner is placed in the centre, and learning is achieved through engaging in different activities. One method of active learning is experiential learning, the philosophy of which can be summarized as “learning by doing”. In this context, learning is considered as a continuous process in which the role of experience and reflection is emphasized. Experiential learning can be applied through many forms such as project-based learning, problem-based learning, simulations, or games.
Based on the concept of experiential learning, the chair of Sustainable Electric Networks and Sources of Energy (SENSE) developed the digital learning platforms "Smart.Grid App" and "Real-Time Lab for the Energy Transition". The learning platforms include interactive games and real-time simulations and have been adjusted to support teaching the topics related to SMAGRINET.
Smart.Grid App as a preparation tool for students and supplement for lectures
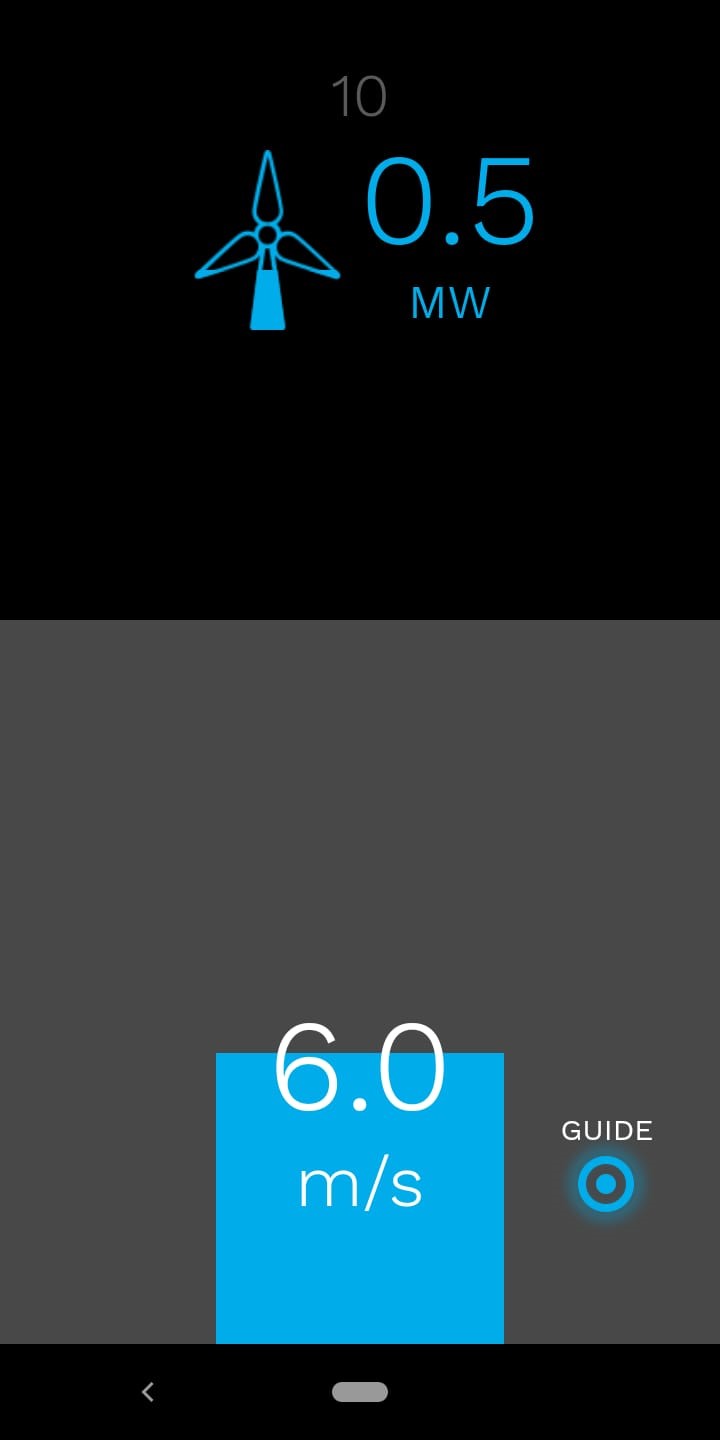
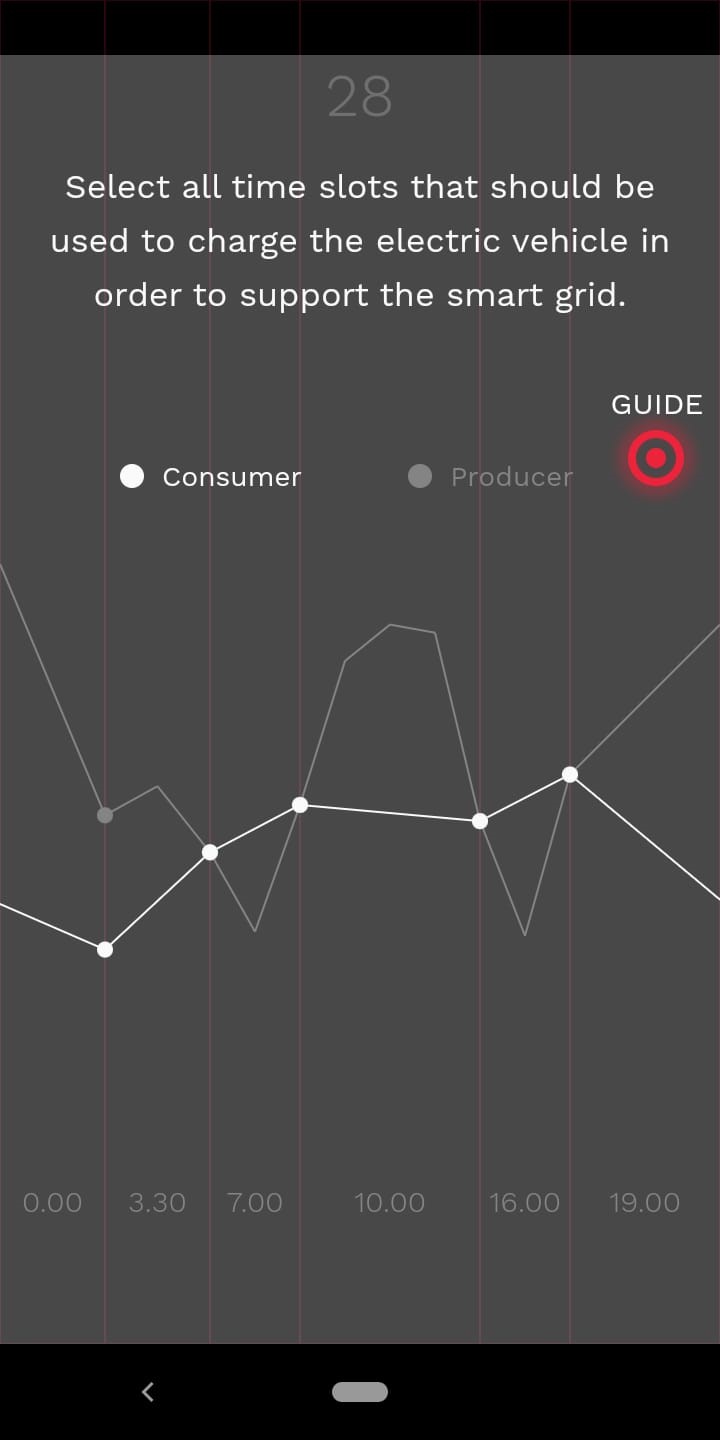
The Smart.Grid App has been designed for smart phones and can be used to prepare students for the lecture or to supplement the content of the lectures. Its unique feature compared to conventional teaching methods is the opportunity to use this app by everyone, anytime and everywhere – just like a smartphone. In five stages, the app user becomes familiar with different components of a smart grid: renewable sources - wind and photovoltaics, storage, flexibility, and energy management.
 |
 |
 |
 |
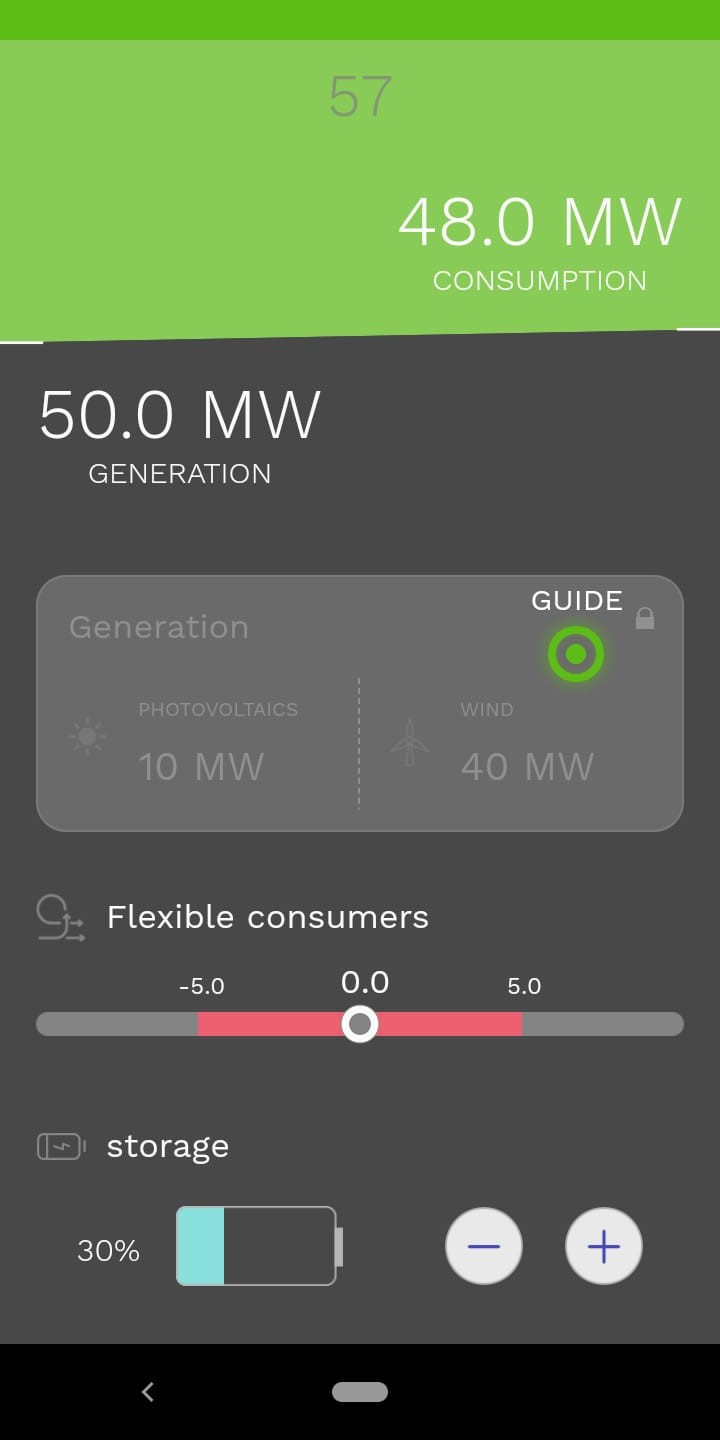 |
Designed as a quiz game, the app motivates students to prove themselves in various areas: In the multiple-choice questions their prior knowledge is assessed, and the interactive tasks require more logical thinking and a little stroke of luck. The following explanatory texts provide students with further information to deepen and augment their understanding of the operation of a smart grid.
Real-Time Lab as interactive support and supplement for lectures
The Real-Time Lab for the Energy Transition is used to support lectures. It includes a web-based visualization platform that communicates and interacts directly with the hardware in the Smart Grid Laboratory at the TU Berlin. The platform is used to run simulations of energy systems as well as to control laboratory components, including inverters, batteries, and a power-to-heat plant. The visualization platform itself is divided into three areas: “learn”, “experience” and “explore” which build on one another and examine relevant topics in progressively greater detail and complexity.
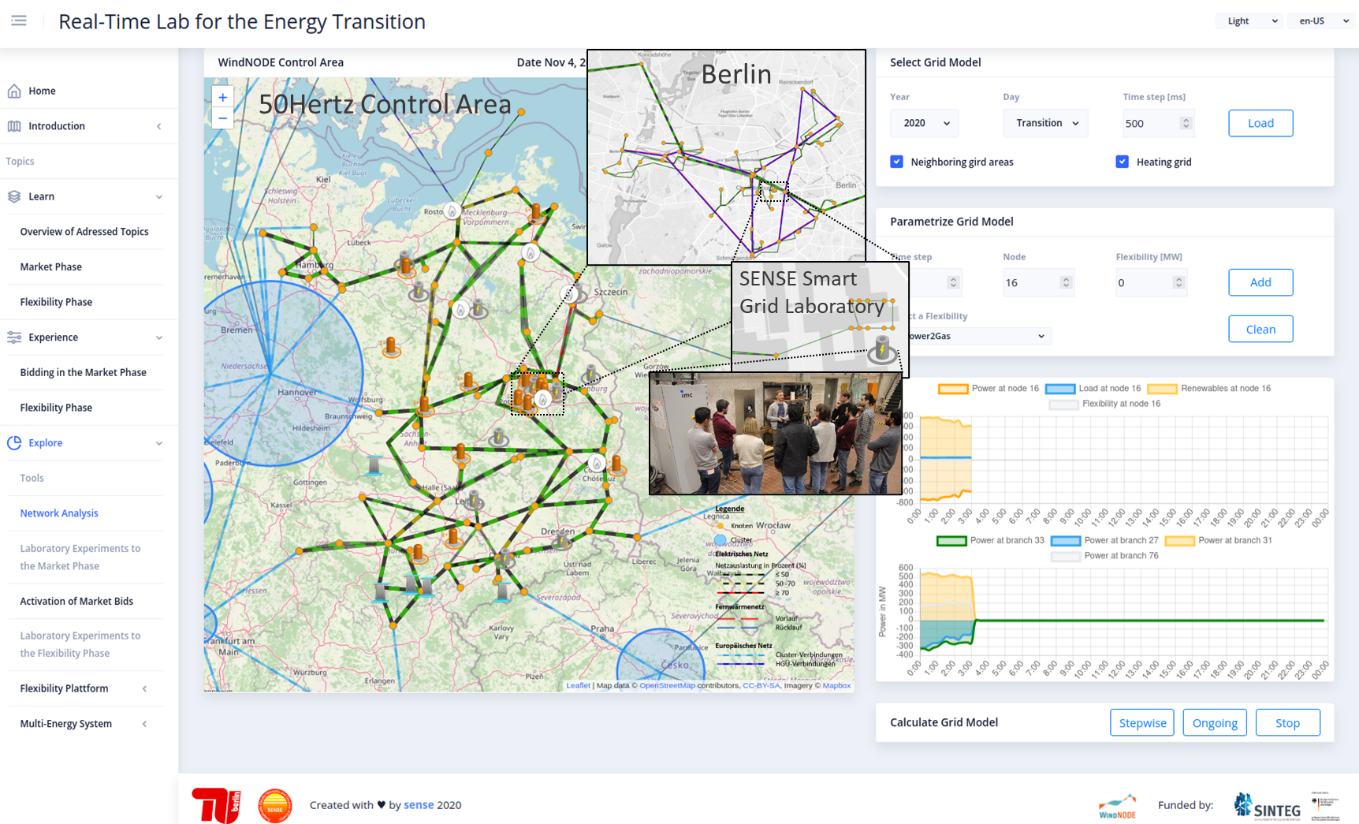
The section "learn" offers the technical and economic fundamentals of the energy system. For example, the "market phase" shows how power is traded on the electricity exchange. In the "flexibility phase", the trading results are explained in terms of the technical aspects of their implementation in grid operation.
The “market phase” and the “flexibility phase” are further explored in the section “experience” with the help of interactive games. Here, students can trade flexibilities – that is, particularly flexible electricity generation or consumption systems – in the “market phase” and use them for congestion management in the "flexibility phase".
In the section "research", physical laboratory components become part of the simulation in order to test innovative concepts of grid operation on a laboratory scale and in real time. These featured innovations are based on the latest research in the field and include power-to-heat and power-to-mobility, as well as integrated market and grid operation management, which makes it possible to utilise flexibilities more efficiently.



